What is NMN?
The science behind NMN and its anti-aging properties
NMN, also known as nicotinamide mononucleotide, is a naturally occurring molecule that has become increasingly popular for its anti-aging properties. In recent years, scientists have conducted extensive research into the effects of NMN on aging processes and the results have been incredibly promising. In this blog post, we will explore the science behind NMN and its potential to help slow down the aging process.
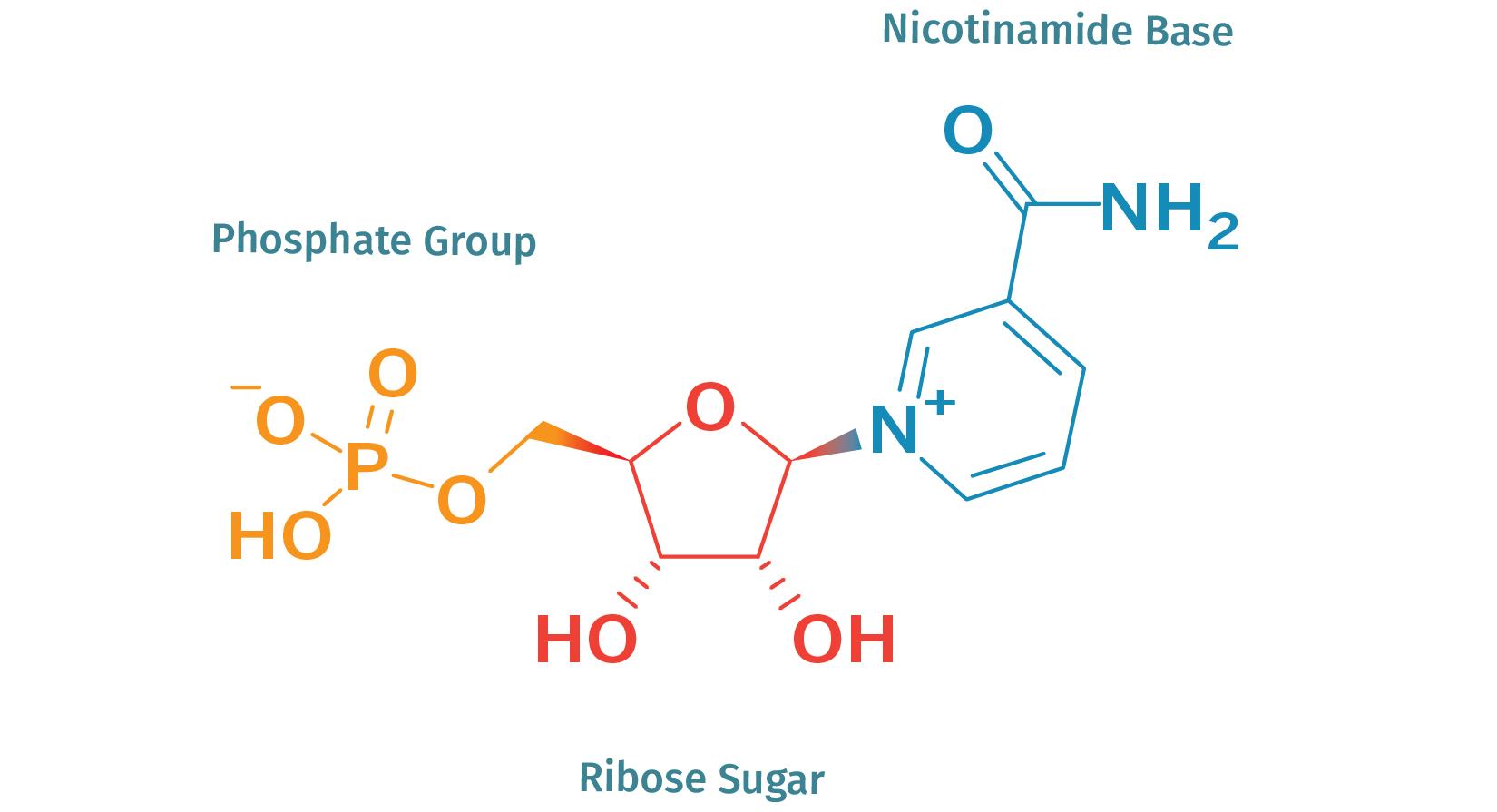
What is NMN?
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) is a molecule that plays a critical role in the body's energy production processes. As a precursor to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), it helps to increase the levels of this essential molecule within cells. NAD+ is an important cofactor in many cellular reactions, including those involved in energy metabolism and DNA repair. By increasing NAD+ levels, NMN can help to support healthy aging and may provide a variety of other benefits to the body.
How does NMN work?
NMN is a molecule that is converted into nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) in the body. NAD+ is an essential molecule that is involved in various biological processes, such as energy production, DNA repair, and gene expression.
As we age, our NAD+ levels decline, which can contribute to cellular dysfunction and lead to age-related diseases. NMN supplementation has been shown to increase NAD+ levels in the body, leading to a range of potential health benefits.
NMN is absorbed into the bloodstream and transported to various tissues, where it is taken up by cells. Inside the cell, NMN is converted into NAD+ through a series of enzymatic reactions. Once NAD+ is formed, it can participate in a range of metabolic processes that support healthy cellular function.
Supports healthy aging
Some of the ways that NAD+ supports healthy aging include:
- Energy production: NAD+ is a key cofactor in the production of ATP, the molecule that provides energy to our cells.
- DNA repair: NAD+ is involved in the repair of DNA damage that can occur over time.
- Gene expression: NAD+ can regulate the expression of genes involved in various cellular processes, such as inflammation and stress response.
By increasing NAD+ levels, NMN supplementation may help to support healthy aging and protect against age-related diseases. However, more research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms behind these potential benefits.
What are the benefits of taking NMN?
As we age, our bodies naturally produce less NAD+, leading to a decline in cellular function. However, supplementing with NMN can help increase NAD+ levels, resulting in several benefits.
One of the main benefits of NMN is its anti-aging properties. NMN has been shown to improve cellular health, increase energy levels, and improve cognitive function. It may also help reduce the risk of age-related diseases, such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease.
Positive Effect
NMN has also been shown to have positive effects on metabolic function, including improving insulin sensitivity, increasing fat oxidation, and reducing inflammation. This can help improve overall health and potentially reduce the risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes, and other metabolic disorders.
Additionally, NMN has been studied for its potential benefits in exercise performance and recovery. It may help improve muscle function, increase endurance, and reduce fatigue during physical activity.
While more research is needed, early studies suggest that NMN may have potential benefits in many areas of health and aging. As always, it's important to speak with your healthcare provider before starting any new supplements.
Are there any side effects of taking NMN?
Like with any supplement, it is important to be aware of potential side effects when taking NMN. The good news is that, so far, no serious side effects have been reported from taking NMN.
One potential side effect of taking NMN is gastrointestinal distress, such as nausea, diarrhea, or stomach cramps. This is often temporary and can be alleviated by taking NMN with food or reducing the dosage.
Blood Pressure
Another possible side effect is a decrease in blood pressure. This is because NMN promotes the relaxation of blood vessels, which can cause a drop in blood pressure. If you have low blood pressure or are taking medication for hypertension, you should speak with your doctor before taking NMN.
Research
It is important to note that there is limited research on the long-term effects of NMN supplementation, so it is not clear if there are any potential risks associated with taking NMN over an extended period of time.
As with any supplement, it is always best to consult with a healthcare professional before beginning to take NMN to ensure that it is safe for you and won't interact with any other medications or health conditions you may have.
How much NMN should I take?
As with any supplement, the appropriate dosage of NMN varies depending on the individual. While there is no official recommended daily intake for NMN, most studies use dosages ranging from 250mg to 1000mg per day.
It's always best to start with a low dose and gradually increase it until you reach the desired effect. It's important to note that higher doses don't necessarily mean better results and may even lead to unwanted side effects.
It's recommended to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen. They can help determine the appropriate dosage for your specific needs and ensure that it's safe to take in combination with any medications or existing health conditions.
Ultimately, finding the right dosage of NMN for your body requires a bit of experimentation and patience. Start with a low dose and give your body time to adjust before increasing it gradually. Remember, slow and steady wins the race!
How Does the Body Make Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+)?
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+) is a coenzyme found in all living cells that plays a crucial role in energy metabolism and cellular communication. Our bodies make NAD+ from the vitamin niacin (vitamin B3) or through the salvage pathway using Nicotinamide Riboside (NR) or Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN).
In the first pathway, our bodies convert niacin to nicotinamide, which is then used to create NAD+. This conversion process requires an enzyme called nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (NAMPT) which is primarily found in our cells' cytosol and is also responsible for the biosynthesis of NAD+ precursors such as NR and NMN.
NAD+
In the salvage pathway, NR or NMN is converted into NAD+ through a series of enzymatic reactions. NR is converted into NMN by the enzyme nicotinamide riboside kinase (NRK) and then NMN is converted into NAD+ by the enzyme nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyltransferase (NMNAT).
The ability of our bodies to make NAD+ declines with age due to the depletion of NR and NMN precursors. This is why supplementing with NMN or NR is becoming an increasingly popular way of boosting NAD+ levels and, by extension, slowing down the aging process.

How is NMN Synthesized In the Body?
NMN, or Nicotinamide Mononucleotide, is a naturally occurring compound in our bodies that plays a critical role in our cells' energy production. NMN is synthesized in our bodies from a precursor called nicotinamide riboside (NR). NR is a form of vitamin B3 that is found in various foods, including milk, meat, and green vegetables.
When we consume foods that contain NR, it is broken down into NMN in our body through a series of enzymatic reactions. These reactions involve the conversion of NR to NMN via the enzyme nicotinamide riboside kinase (NRK) and then the conversion of NMN to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) via the enzyme nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyltransferase (NMNAT).
Essential Coenzyme
NAD+ is an essential coenzyme in our cells that is involved in numerous biological processes, including DNA repair, gene expression, and energy metabolism. NMN is a critical precursor for NAD+ biosynthesis, and research suggests that increasing NMN levels in the body can boost NAD+ levels and provide numerous benefits.
Supplementing with NMN has been shown to increase NAD+ levels in cells and tissues, which can lead to a range of benefits, including improved energy metabolism, enhanced DNA repair, and even anti-aging effects.
However, it is important to note that our body's ability to synthesize NMN and NAD+ decreases as we age, which is one reason why supplementing with NMN may become increasingly important as we get older.
Overall, NMN plays a vital role in the body's energy production and overall health. Understanding how NMN is synthesized in the body can help us appreciate the importance of maintaining healthy levels of this essential compound.
NMN Side Effects and Safety
While NMN has been shown to have numerous potential benefits for human health, it is important to understand the potential side effects and safety considerations of taking this supplement.
Research has shown that NMN is generally safe for human consumption and does not cause any significant adverse effects in healthy individuals. However, it is important to note that there have not been many long-term studies conducted on the safety of NMN, and the potential for adverse effects over time is still not fully understood.
Minor Side Effects
In some studies, participants have reported minor side effects such as headaches, dizziness, and gastrointestinal distress. These side effects are typically mild and short-lived, and they usually subside after a few days of taking the supplement.
It is important to note that NMN is still a relatively new supplement, and its long-term safety is not fully understood. While early research has been promising, more research is needed to determine the long-term safety of this supplement.
Speak With Your Doctor
If you are considering taking NMN, it is important to speak with your healthcare provider first. They can help you determine if this supplement is safe and appropriate for your individual health needs.
Overall, while there are some potential side effects associated with NMN, this supplement appears to be safe for most individuals when taken at appropriate doses. As with any supplement or medication, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before beginning use.
The History of NMN and NAD+
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+) was first discovered in 1906 by Arthur Harden and William John Young in yeast. However, it wasn't until 1936 that Sir Arthur Harden and his colleagues discovered the structure of NAD+. They also found that NAD+ is a crucial coenzyme for many metabolic pathways.
As research into NAD+ continued, scientists discovered that it is essential for maintaining the health of all living cells. However, NAD+ levels in our bodies decrease as we age, leading to a decline in metabolic functions and an increased risk of age-related diseases.
In 2004, Dr. Shin-ichiro Imai and his colleagues discovered that supplementing with nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) can boost NAD+ levels in the body. This groundbreaking discovery has led to further research into the anti-aging properties of NMN and NAD+.
Since then, several studies have shown that NMN can help improve metabolic function, increase energy levels, and improve the function of various organs such as the liver, muscles, and brain. Additionally, researchers have also found that NMN can help slow down the aging process and improve lifespan in animal studies.
The discovery of NMN has led to exciting developments in the field of anti-aging research. It is hoped that with further research, NMN may be able to help humans live healthier, longer lives.


